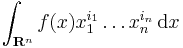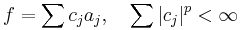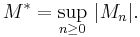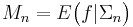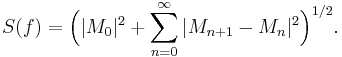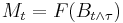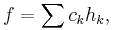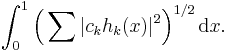Hardy space
In complex analysis, the Hardy spaces (or Hardy classes) Hp are certain spaces of holomorphic functions on the unit disk or upper half plane. They were introduced by Frigyes Riesz (Riesz 1923), who named them after G. H. Hardy, because of the paper (Hardy 1915). In real analysis Hardy spaces are certain spaces of distributions on the real line, which are (in the sense of distributions) boundary values of the holomorphic functions of the complex Hardy spaces, and are related to the Lp spaces of functional analysis. For 1 ≤ p ≤ ∞ these real Hardy spaces Hp are certain subsets of Lp, while for p < 1 the Lp spaces have some undesirable properties, and the Hardy spaces are much better behaved.
There are also higher dimensional generalizations, consisting of certain holomorphic functions on tube domains in the complex case, or certain spaces of distributions on Rn in the real case.
Hardy spaces have a number of applications in mathematical analysis itself, as well as in control theory (such as H∞ methods) and in scattering theory.
Contents |
Hardy spaces for the unit disk
For spaces of holomorphic functions on the open unit disk, the Hardy space H2 consists of the functions ƒ whose mean square value on the circle of radius r remains bounded as r → 1 from below.
More generally, the Hardy space Hp for 0 < p < ∞ is the class of holomorphic functions f on the open unit disk satisfying
This class Hp is a vector space. The number on the left side of the above inequality is the Hardy space p-norm for f, denoted by 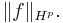 It is a norm when p ≥ 1, but not when 0 < p < 1.
It is a norm when p ≥ 1, but not when 0 < p < 1.
The space H∞ is defined as the vector space of bounded holomorphic functions on the disk, with the norm
For 0 < p ≤ q ≤ ∞, the class Hq is a subset of Hp, and the Hp-norm is increasing with p (it is a consequence of Hölder's inequality that the Lp-norm is increasing for probability measures, i.e. measures with total mass 1).
Hardy spaces on the unit circle
The Hardy spaces defined in the preceding section can also be viewed as certain closed vector subspaces of the complex Lp spaces on the unit circle. This connection is provided by the following theorem (Katznelson 1976, Thm 3.8): Given f ∈ Hp, with p > 0, the radial limit
exists for almost every θ. The function 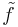 belongs to the Lp space for the unit circle, and one has that
belongs to the Lp space for the unit circle, and one has that
Denoting the unit circle by T, and by Hp(T) the vector subspace of Lp(T) consisting of all limit functions 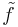 , when f varies in Hp, one then has that for p ≥ 1,
, when f varies in Hp, one then has that for p ≥ 1,
(Katznelson 1976), where the ĝ(n) are the Fourier coefficients of a function g integrable on the unit circle,
The space Hp(T) is a closed subspace of Lp(T). Since Lp(T) is a Banach space (for 1 ≤ p ≤ ∞), so is Hp(T).
The above can be turned around. Given a function 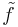 ∈ Lp(T), with p ≥ 1, one can regain a (harmonic) function f on the unit disk by means of the Poisson kernel Pr:
∈ Lp(T), with p ≥ 1, one can regain a (harmonic) function f on the unit disk by means of the Poisson kernel Pr:
and f belongs to Hp exactly when 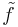 is in Hp(T). Supposing that
is in Hp(T). Supposing that 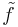 is in Hp(T). i.e. that
is in Hp(T). i.e. that 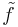 has Fourier coefficients (an)n ∈ Z with an = 0 for every n < 0, then the element f of the Hardy space Hp associated to
has Fourier coefficients (an)n ∈ Z with an = 0 for every n < 0, then the element f of the Hardy space Hp associated to 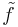 is the holomorphic function
is the holomorphic function
In applications, those functions with vanishing negative Fourier coefficients are commonly interpreted as the causal solutions. Thus, the space H2 is seen to sit naturally inside L2 space, and is represented by infinite sequences indexed by N; whereas L2 consists of bi-infinite sequences indexed by Z.
Connection to real Hardy spaces on the circle
When 1 ≤ p < ∞, the real Hardy spaces Hp discussed further down in this article are easy to describe in the present context. A real function f on the unit circle belongs to the real Hardy space Hp(T) if it is the real part of a function in Hp(T), and a complex function f belongs to the real Hardy space iff Re f and Im f belong to the space (see the section on real Hardy spaces below).
For p < 1, such tools as Fourier coefficients, Poisson integral, conjugate function, are no longer valid. For example, consider
The function F is in Hp for every p < 1, the radial limit f is in Hp(T) but its real part Re f is 0 almost everywhere. It is no longer possible to recover F from Re f, and one cannot define real-Hp(T) in the simple way above.
For the same function F, let fr (ei θ) = F(r ei θ). The limit when r → 1 of Re fr, in the sense of distributions on the circle, is a non-zero multiple of the Dirac distribution at z = 1. The Dirac distribution at any point of the unit circle belongs to real-Hp(T) for every p < 1 (see below).
Factorization into inner and outer functions (Beurling)
For 0 < p ≤ ∞, every non-zero function ƒ in Hp can be written as the product ƒ = Gh where G is an outer function and h is an inner function, as defined below (Rudin 1987, Thm 17.17). This "Beurling factorization" allows the Hardy space to be completely characterized by the spaces of inner and outer functions.
One says that G(z) is an outer (exterior) function if it takes the form
for some complex number c with |c| = 1, and some positive measurable function φ on the unit circle such that log φ is integrable on the circle. In particular, when φ is integrable on the circle, G is in H1 because the above takes the form of the Poisson kernel (Rudin 1987, Thm 17.16). This implies that
for almost every θ.
One says that h(z) is an inner (interior) function if and only if |h(z)| ≤ 1 on the unit disk and the limit
exists for almost all θ and its modulus is equal to 1. In particular, h is in H∞. The inner function can be further factored into a form involving a Blaschke product.
The function f, decomposed as f = Gh, is in Hp if and only if the positive function φ belongs to Lp(T), where φ is the function in the representation of the outer function G.
Let G be an outer function represented as above from a function φ on the circle. Replacing φ by φα, α > 0, a family (Gα) of outer functions is obtained, with the properties:
-
- G1 = G, Gα+β = Gα Gβ and |Gα| = |G|α almost everywhere on the circle.
It follows that whenever 0 < p, q, r < ∞ and 1/r = 1/p + 1/q, every function f in Hr can be expressed as the product of a function in Hp and a function in Hq. For example: every function in H1 is the product of two functions in H2; every function in Hp, p < 1, can be expressed as product of several functions in some Hq, q > 1.
Real-variable techniques on the unit circle
Real-variable techniques, mainly associated to the study of real Hardy spaces defined on Rn (see below), are also used in the simpler framework of the circle. It is a common practice to allow for complex functions (or distributions) in these "real" spaces. The definition that follows does not distinguish between real or complex case.
Let Pr denote the Poisson kernel on the unit circle T. For a distribution f on the unit circle, set
where the star indicates convolution between the distribution f and the function ei θ → Pr(θ) on the circle. Namely, (f ∗ Pr)(ei θ) is the result of the action of f on the C∞-function defined on the unit circle by
For 0 < p < ∞, the real Hardy space Hp(T) consists of distributions f such that M f is in Lp(T).
The function F defined on the unit disk by F(r ei θ) = (f ∗ Pr)(ei θ) is harmonic, and M f is the radial maximal function of F. When M f belongs to Lp(T) and p ≥ 1, the distribution f "is" a function in Lp(T), namely the boundary value of F. For p ≥ 1, the real Hardy space Hp(T) is a subset of Lp(T).
Conjugate function
To every real trigonometric polynomial u on the unit circle, one associates the real conjugate polynomial v such that u + iv extends to a holomorphic function in the unit disk,
This mapping u → v extends to a bounded linear operator H on Lp(T), when 1 < p < ∞ (up to a scalar multiple, it is the Hilbert transform on the unit circle), and H also maps L1(T) to weak-L1(T). When 1 ≤ p < ∞, the following are equivalent for a real valued integrable function f on the unit circle:
- the function f is the real part of some function g ∈ Hp(T)
- the function f and its conjugate H(f) belong to Lp(T)
- the radial maximal function M f belongs to Lp(T).
When 1 < p < ∞, H(f) belongs to Lp(T) when f ∈ Lp(T), hence the real Hardy space Hp(T) coincides with Lp(T) in this case. For p = 1, the real Hardy space H1(T) is a proper subspace of L1(T).
The p = ∞ case was excluded from the definition of real Hardy spaces, because the maximal function M f of an L∞ function is always bounded, and because it is not desirable that real-H∞ be equal to L∞. However, the two following properties are equivalent for a real valued function f
- the function f is the real part of some function g ∈ H∞(T)
- the function f and its conjugate H(f) belong to L∞(T).
Real Hardy spaces when 0 < p < 1
When 0 < p < 1, a function F in Hp cannot be reconstructed from the real part of his boundary limit function on the circle, because of the lack of convexity of Lp in this case. Convexity fails but a kind of "complex convexity" remains, namely the fact that z → |z|q is subharmonic for every q > 0. As a consequence, if
is in Hp, it can be shown that cn = O(n1/p–1). It follows that the Fourier series
converges in the sense of distributions to a distribution f on the unit circle, and F(r ei θ) = (f ∗ Pr)(θ). The function F ∈ Hp can be reconstructed from the real distribution Re f on the circle, because the Taylor coefficients cn of F can be computed from the Fourier coefficients of Re f : distributions on the circle are general enough for handling Hardy spaces when p < 1. Distributions do appear, as it is seen with functions F(z) = (1 – z)–N (for |z| < 1), that belong to Hp when 0 < N p < 1 (and N an integer ≥ 1).
A real distribution on the circle belongs to real-Hp(T) iff it is the boundary value of the real part of some F ∈ Hp. A Dirac distribution δx, at any point x of the unit circle, belongs to real-Hp(T) for every p < 1; derivatives δ ’x belong when p < 1/2, second derivatives δ ’’x when p < 1/3, and so on.
Hardy spaces for the upper half plane
It is possible to define Hardy spaces on other domains than the disc, and in many applications Hardy spaces on a complex half-plane (usually the right half-plane or upper half-plane) are used.
The Hardy space 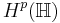 on the upper half-plane
on the upper half-plane 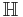 is defined to be the space of holomorphic functions f on
is defined to be the space of holomorphic functions f on 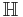 with bounded (quasi-)norm, the norm being given by
with bounded (quasi-)norm, the norm being given by
The corresponding 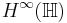 is defined as functions of bounded norm, with the norm given by
is defined as functions of bounded norm, with the norm given by
Although the unit disk 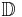 and the upper half-plane
and the upper half-plane 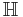 can be mapped to one-another by means of Möbius transformations, they are not interchangeable as domains for Hardy spaces. Contributing to this difference is the fact that the unit circle has finite (one-dimensional) Lebesgue measure while the real line does not. However, for H2, one may still state the following theorem: Given the Möbius transformation
can be mapped to one-another by means of Möbius transformations, they are not interchangeable as domains for Hardy spaces. Contributing to this difference is the fact that the unit circle has finite (one-dimensional) Lebesgue measure while the real line does not. However, for H2, one may still state the following theorem: Given the Möbius transformation 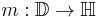 with
with
then there is an isometric isomorphism
with
Real Hardy spaces for Rn
In analysis on the real vector space Rn, the Hardy space Hp (for 0 < p ≤ ∞) consists of tempered distributions ƒ such that for some Schwartz function Φ with ∫Φ = 1, the maximal function
is in Lp(Rn), where ∗ is convolution and Φt(x) = t−nΦ(x/t). The Hp-quasinorm ||ƒ||Hp of a distribution ƒ of Hp is defined to be the Lp norm of MΦƒ (this depends on the choice of Φ, but different choices of Schwartz functions Φ give equivalent norms). The Hp-quasinorm is a norm when p ≥ 1, but not when p < 1.
If 1 < p < ∞, the Hardy space Hp is the same vector space as Lp, with equivalent norm. When p = 1, the Hardy space H1 is a proper subspace of L1. One can find sequences in H1 that are bounded in L1 but unbounded in H1, for example on the line
The L1 and H1 norms are not equivalent on H1, and H1 is not closed in L1. The dual of H1 is the space BMO of functions of bounded mean oscillation. The space BMO contains unbounded functions (proving again that H1 is not closed in L1).
If p < 1 then the Hardy space Hp has elements that are not functions, and its dual is the homogeneous Lipschitz space of order n(1/p − 1). When p < 1, the Hp-quasinorm is not a norm, as it is not subadditive. The pth power ||ƒ||Hpp is subadditive for p < 1 and so defines a metric on the Hardy space Hp, which defines the topology and makes Hp into a complete metric space.
Atomic decomposition
When 0 < p ≤ 1, a bounded measurable function ƒ of compact support is in the Hardy space Hp if and only if all its moments
whose order i1 + ··· + in is at most n(1/p − 1) vanish. For example, the integral of f must vanish in order that f ∈ Hp, 0 < p ≤ 1, and as long as p > n/(n+1) this is also sufficient.
If in addition ƒ has support in some ball B and is bounded by |B| −1/p then ƒ is called an Hp-atom (here |B| denotes the Euclidean volume of B in Rn). The Hp-quasinorm of an arbitrary Hp-atom is bounded by a constant depending only on p and on the Schwartz function Φ.
When 0 < p ≤ 1, any element f of Hp has an atomic decomposition as a convergent infinite combination of Hp-atoms,
where the aj are Hp-atoms and the cj are scalars.
On the line for example, the difference of Dirac distributions f = δ1 − δ0 can be represented as a series of Haar functions, convergent in Hp-quasinorm when 1/2 < p < 1 (on the circle, the corresponding representation is valid for 0 < p < 1, but on the line, Haar functions do not belong to Hp when p ≤ 1/2 because their maximal function is equivalent at infinity to a x–2 for some a ≠ 0).
Martingale Hp
Let (Mn)n ≥ 0 be a martingale on some probability space (Ω, Σ, P), with respect to an increasing sequence of σ-fields (Σn)n ≥ 0. Assume for simplicity that Σ is equal to the σ-field generated by the sequence (Σn)n ≥ 0. The maximal function of the martingale is defined by
Let 1 ≤ p < ∞. The martingale (Mn)n ≥ 0 belongs to martingale-Hp when M∗ ∈ Lp.
If M∗ ∈ Lp, the martingale (Mn)n ≥ 0 is bounded in Lp, hence it converges almost surely to some function f by the martingale convergence theorem. Moreover, Mn converges to f in Lp-norm by the dominated convergence theorem, hence Mn can be expressed as conditional expectation of f on Σn. It is thus possible to identify martingale-Hp with the subspace of Lp(Ω, Σ, P) consisting of those f such that the martingale
belongs to martingale-Hp.
Doob's maximal inequality implies that martingale-Hp coincides with Lp(Ω, Σ, P) when 1 < p < ∞. The interesting space is martingale-H1, whose dual is martingale-BMO (Garsia 1973).
The Burkholder–Gundy inequalities (when p > 1) and the Burgess Davis inequality (when p = 1) relate the Lp-norm of the maximal function to that of the square function of the martingale
Martingale-Hp can be defined by saying that S(f) ∈ Lp (Garsia 1973).
Martingales with continuous time parameter can also be considered. A direct link with the classical theory is obtained via the complex Brownian motion (Bt) in the complex plane, starting from the point z = 0 at time t = 0. Let τ denote the hitting time of the unit circle. For every holomorphic function F in the unit disk,
is a martingale, that belongs to martingale-Hp iff F ∈ Hp (Burkholder, Gundy & Silverstein 1971).
Example: dyadic martingale-H1
In this example, Ω = [0, 1] and Σn is the finite field generated by the dyadic partition of [0, 1] into 2n intervals of length 2−n, for every n ≥ 0. If a function f on [0, 1] is represented by its expansion on the Haar system (hk)
then the martingale-H1 norm of f can be defined by the L1 norm of the square function
This space, sometimes denoted by H1(δ), is isomorphic to the classical real H1 space on the circle (Müller 2005). The Haar system is an unconditional basis for H1(δ).
References
- Burkholder, Donald L.; Gundy, Richard F.; Silverstein, Martin L. (1971), "A maximal function characterization of the class Hp", Trans. Amer. Math. Soc. (Transactions of the American Mathematical Society, Vol. 157) 157: 137–153, doi:10.2307/1995838, JSTOR 1995838. MR0274767
- Cima, Joseph A.; Ross, William T. (2000), The Backward Shift on the Hardy Space, American Mathematical Society, ISBN 0-8218-2083-4
- Colwell, Peter (1985), Blaschke Products - Bounded Analytic Functions, Ann Arbor: University of Michigan Press, ISBN 0-472-10065-3
- Duren, P. (1970), Theory of Hp-Spaces, New York: Academic Press
- Fefferman, Charles; Stein, Elias M. (1972), "Hp spaces of several variables", Acta Math. 129 (3–4): 137–193, doi:10.1007/BF02392215. MR0447953
- Folland, G.B. (2001), "Hardy spaces", in Hazewinkel, Michiel, Encyclopedia of Mathematics, Springer, ISBN 978-1556080104, http://www.encyclopediaofmath.org/index.php?title=H/h110090
- Garsia, Adriano M. (1973), Martingale inequalities: Seminar notes on recent progress, Mathematics Lecture Notes Series, Reading, Mass.-London-Amsterdam: W. A. Benjamin, Inc., pp. viii+184 MR0448538
- Hardy, G. H. (1915), "On the mean value of the modulus of an analytic function", Proceedings of the London mathematical society series 2 14: 269–277
- Hoffman, Kenneth (1988), Banach spaces of analytic functions, New York: Dover Publications, ISBN 0-486-65785-X
- Katznelson, Yitzhak (1976), An introduction to Harmonic Analysis, Dover, ISBN 0-486-63331-4
- Müller, Paul F. X. (2005), Isomorphisms between H1 spaces, Basel: Mathematics Institute of the Polish Academy of Sciences. Mathematical Monographs (New Series), Birkhäuser Verlag, pp. xiv+453, ISBN 978-3-7643-2431-5 MR2157745
- Riesz, F. (1923), "Über die Randwerte einer analytischen Funktion", Math. Z. 18: 87–95, doi:10.1007/BF01192397
- Mashreghi, J. (2009), Representation Theorems in Hardy Spaces, Cambridge University Press
- Rudin, Walter (1987), Real and Complex Analysis, McGraw-Hill, ISBN 0-07-100276-6
- Shvedenko, S.V. (2001), "Hardy classes", in Hazewinkel, Michiel, Encyclopedia of Mathematics, Springer, ISBN 978-1556080104, http://www.encyclopediaofmath.org/index.php?title=h/h046320
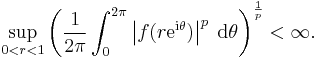
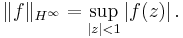
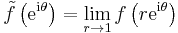
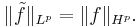
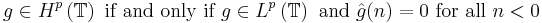
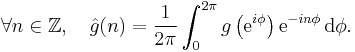
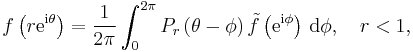
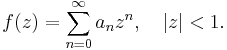
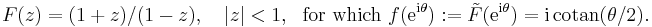
![G(z) = c \, \exp\left[\frac{1}{2\pi} \int_{-\pi}^{\pi}
\frac{\mathrm{e}^{i\theta}%2Bz}{\mathrm{e}^{i\theta}-z} \log \varphi(\mathrm{e}^{i\theta}) \, \mathrm{d}\theta \right]](/2012-wikipedia_en_all_nopic_01_2012/I/6f7bad5c07817f6b8700f54375d14528.png)
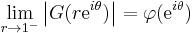
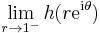
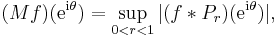
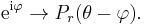
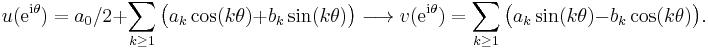
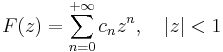
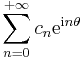
![\|f\|_{H^p} = \sup_{y>0} \left[ \int|f(x%2B \mathrm{i} \, y)|^p\, \mathrm{d}x \right]^{1/p}.](/2012-wikipedia_en_all_nopic_01_2012/I/b15a0d97f1b706425d91e9e3c0467c4b.png)
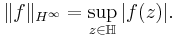
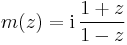
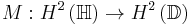
=\frac{\sqrt{\pi}}{(1-z)} \, f(m(z)).](/2012-wikipedia_en_all_nopic_01_2012/I/c9323665c28f5c7d876abdfe8979349f.png)
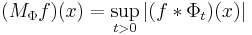
![f_k(x) = \mathbf{1}_{[0, 1]}(x - k) - \mathbf{1}_{[0, 1]}(x - k).](/2012-wikipedia_en_all_nopic_01_2012/I/190e73e9ba54e68c26e8a2616ab8ca54.png)